Basically, Kotlin attempts to resolve NullPointerException(NPE) by making the data types as nou nullable
Variable Declaration
If you try to assign a null value to a variable, the following compile error will be thrown by IDE
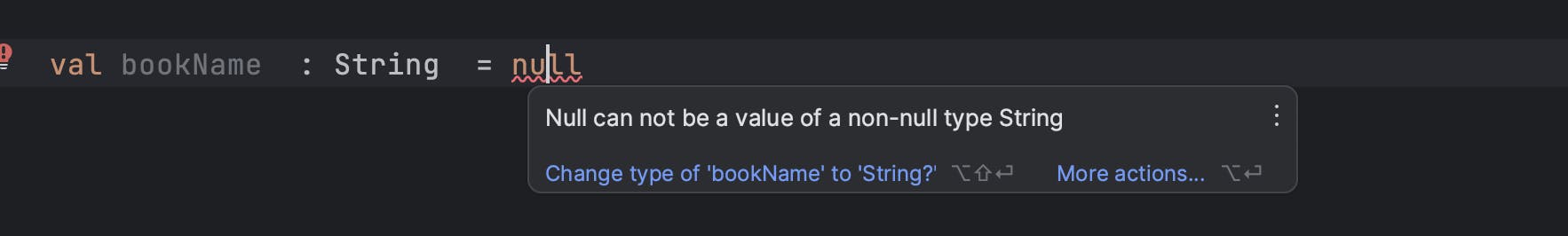
To make the variable nullable, we can declare as follows
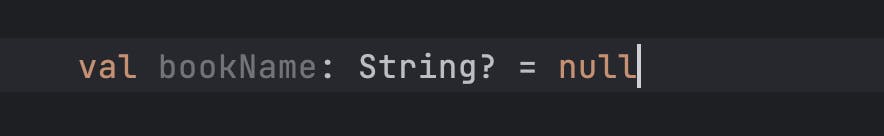
Accessing null Variable
If you access the null variable, you will get the following compile error
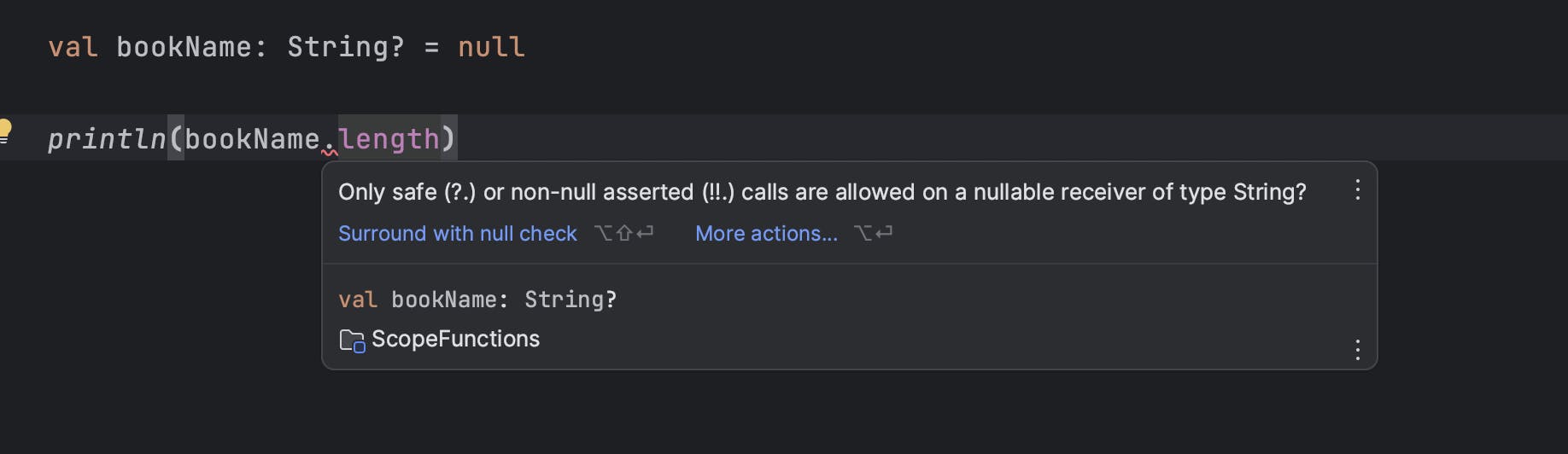
Safe Operator -?
? - using this operator, we can access the null variable as follows
val bookName: String? = null
println(bookName?.length) // prints null
bookName?.length does the following
println(bookName?.length) // prints null
if (bookName == null) {
println(null)
} else {
println(bookName.length)
}
Elvis Operator - ?:
The Elvis operator is used to simplify the code while using the nullable variable as follows
val bookName: String? = null
// elvis operator
println(bookName ?: "bookName is null") // prints bookName is null
/*
Elvis operator does the following
*/
if (bookName != null) {
println(bookName)
} else {
println("bookName is null")
}
The Left side of Elvis operator is executed if the bookName is not null
The Right side of Elvis operator is executed if the bookName is null
!! Operator
!! operator executes the null variable without checking the variable is null which is if you want to have NPE, then you can use the variable as follows
val bookName: String? = null
println(bookName!!.length) // throws NPE
Nullable Receiver
you can specify behavior for null values without the need to use null-checking logic at each call-site.
For example, let's take a look at toString() extension function
fun Any?.toString(): String {
if (this == null) return "null"
// after the null check, 'this' is autocast to a non-null type, so the toString() below
// resolves to the member function of the Any class
return toString()
}
So finally, I hope I made somebody understand how Kotlin handles null
Please leave your comments to improve.
Happy and Enjoy coding

